- Home
- Garden Care
- Pest & Disease Control
- Summit Mosquito Dunks (2 packs with 12 in a case) in Bulk
Product Description
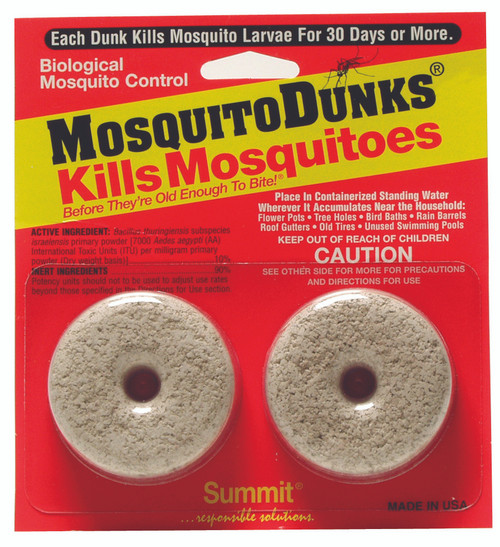
Summit Mosquito Dunks (2 packs with 12 in a case) FREE SHIPPING
SPECIAL BULK PRICING For ORGANIC production and gardening. Biological mosquito control. Each Summit Mosquito Dunks (2 packs with 12 in a case) in bulk kills mosquito larvae for 30 days or more. Can be used in Fish Habitats.
Place in containerized standing water wherever it accumulates near the household: flower pots, tree holes, bird baths, roof gutters, rain barrels, old tires, unused swimming pools, animal watering troughs.
A safe, nontoxic way to control mosquitoes before they become flying, biting, disease-carrying adults.
Summit Mosquito Dunks (2 packs with 12 in a case) in bulk-Kills Mosquitoes Before They're Old Enough To BiteTM.
How to Prevent Zika, West Nile and other Mosquito-Borne Viruses
The key to disease prevention is controlling mosquito breeding grounds to prevent mosquito bites Zika is the latest virus to garner worldwide headlines, and the Pan American Health Organization has predicted that Zika virus will spread throughout the Americas. Zika virus is transmitted by the bites of infected mosquitoes—as are many deadly and debilitating diseases including West Nile virus, malaria, chikungunya and dengue fever.
The Zika virus is believed to be carried by two species of mosquitoes which are found in the USA—Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti. Zika has already caused more than 1 million known infections in Central and South America. Travelers who have become infected with the Zika virus in other countries have already arrived in the U.S., which raises the possibility of homegrown Zika cases in the U.S. in the future.
Reduce Mosquito Breeding Site
There is no vaccine to prevent the spread of Zika virus, just as there is no vaccine to prevent the spread of West Nile virus. For that reason, experts say the key to controlling the spread of these mosquito-borne diseases is to control mosquito populations.
“An important part of controlling mosquito-borne viruses is being ‘mosquito smart’ and reducing places where mosquitoes can breed,” said Jonathan Cohen, mosquito control expert and President of Summit Responsible Solutions. Mosquitoes lay their eggs in standing water, so homeowners need to be vigilant in eliminating places where water can collect and stand in their yards and gardens.”
To reduce mosquito breeding grounds, dispose of cans, plastic containers, old tires and other items that can collect water. Turn over wheelbarrows and empty children’s wading pools. Clean clogged roof gutters, which can become prime mosquito-breeding pools. Periodically empty the saucers under ceramic pots to make sure they are not harboring mosquito larvae.
Kill Mosquito Larvae with BTI
To prevent mosquitoes from breeding in places where water collects—including ponds, bird baths, animal watering troughs, gutters, tree holes and rain barrels—use a mosquito control product that contains BTI to kill mosquito larvae. BTI (Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis) is a bacterium that naturally kills mosquito larvae before they can grow up to become flying, biting, disease-spreading adults. Even though BTI is deadly to mosquito larvae, it is harmless to people, plants, pets, fish, wildlife and beneficial insects.
BTI is the active ingredient in Mosquito Dunks®, the number-one selling biological mosquito control product. When a donut-shaped Mosquito Dunk® is placed in standing water, the BTI in the Dunk™ will kill mosquito larvae for up to 30 days.
In places where small amounts of water collect—such as tree holes, potted plant saucers and water reservoirs in self-watering planters, a BTI product called Mosquito Bits® is a good way to kill mosquito larvae. Mosquito Bits® granules can be sprinkled into virtually any place where water can collect. Mosquito Bits® can also be used to kill mosquito larvae in swampy areas and larger areas where water cannot be drained. In addition, Mosquito Bits® are highly effective as a “shock treatment” in water where immediate larval control is needed due to an extremely dense population of mosquito larvae, because the Bits release their active ingredient (BTI) all at once. The Mosquito Bits® application can be immediately followed by the addition of Mosquito Dunks® for long-term control.
To kill adult mosquitoes, use a permethrin-based insecticide such as Summit® Mosquito and Gnat Barrier. The permethrin in Summit® Mosquito and Gnat Barrier kills and repels mosquitoes and other insect pests for up to four weeks. Simply attach a garden hose to the hose-end sprayer bottle and spray the yard perimeter and fences, shrubbery, vegetation, or other vertical surfaces where mosquitoes can hide and rest.
Neighborhood Solutions
Controlling mosquitoes in your own backyard is an important part of mosquito control. So is getting your neighbors to be as vigilant in eliminating and controlling mosquito breeding grounds as you are. “Once you’ve reduced mosquito breeding grounds in your backyard and used BTI to kill mosquito larvae, get your neighbors involved in mosquito control, too,” said Cohen. “The mosquitoes in their yard can easily travel into your yard and into the yards of everyone on the block. It’s important for the entire neighborhood to take mosquito control seriously—especially to control the spread of disease.”
Reduce Mosquito Exposure
To reduce the chances of getting mosquito bites, limit your outdoor activities during the times of day when mosquitoes are most active—an hour before and after dawn and an hour before and after dusk. Keep as much of your skin covered as possible by wearing long sleeves and long pants. Wear light-colored clothing, because mosquitoes are attracted to darker colors. Using EPA registered mosquito repellents is another good way to keep mosquitoes—and mosquito bites—at bay. Apply repellent directly to skin or clothing as recommended on the product label. By reducing exposure to mosquitoes, limiting breeding sites and using the most effective types of mosquito control products, you can greatly reduce your chances of being bitten by disease carrying mosquitoes.
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...









